El IoT industrial está transformando el funcionamiento de los entornos de planta al permitir una hiperconexión
redes que aportan valor a través de fábricas inteligentes, mantenimiento predictivo, gestión energética y control remoto
la monitorización, entre otros. Esta tecnología permite a las industrias optimizar la productividad, aumentar la eficiencia y reducir
los costes operativos.
5 Industrial IoT Use Cases to Boost
la eficiencia y reducir costes

Qué significa el IoT industrial para las empresas
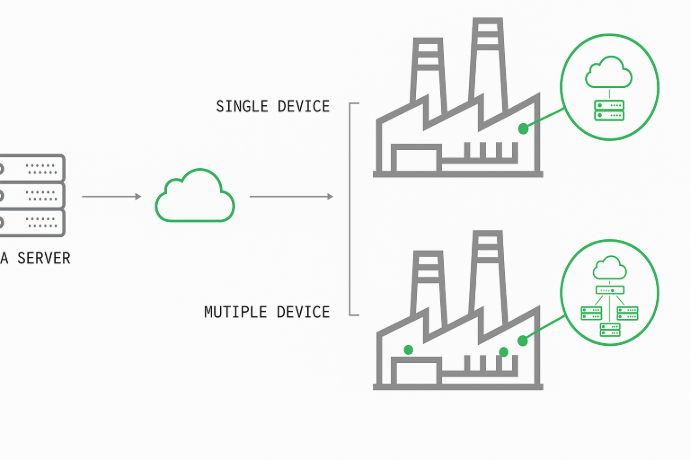
El IoT (Internet de las Cosas), que se refiere a todo tipo de objetos y dispositivos conectados a Internet, ya no es ciencia ficción, sino una realidad que facilita nuestras vidas. Prácticamente cualquier cosa puede conectarse a Internet e interactuar sin intervención humana. Según distintas fuentes, se estimaba que para 2020 habría entre 20 y 50 mil millones de dispositivos conectados, y se espera que esta cifra supere los 125 mil millones para 2030. Las posibles aplicaciones son casi infinitas, y las industrias que adoptan esta tecnología crecen día a día.
Pero el IoT no es solo una tecnología orientada al consumidor para simplificar la vida cotidiana. Hablar de IoT también significa hablar de la Industria 4.0, o lo que conocemos como IIoT (Internet Industrial de las Cosas). Según el Informe de Comunicación Industrial, en 2016 había 90 millones de dispositivos de IoT industrial desplegados en todo el mundo. Se proyectaba que esa cifra creciera hasta los 150 millones en 2021.
Industrial IoT doesn’t necessarily involve large systems or machines managing complex processes. It can also include small sensor based devices that provide data, alerts, and insights enabling simple automated actions or supporting daily business analysis and protocol execution.
5 Ejemplos reales de IoT industrial
- Mantenimiento remoto de infraestructuras: el mantenimiento remoto es esencial para empresas con múltiples sedes operativas o activos distribuidos. Las plataformas IoT que se integran con los sistemas de gestión de edificios (BMS) están creciendo rápidamente. El IoT permite que diferentes sistemas de proveedores de BMS se conecten bajo una sola red, reduciendo los costes de O&M (operación y mantenimiento) al minimizar los desplazamientos innecesarios de técnicos. Empresas como Barbara IoT están liderando este ámbito con soluciones de infraestructura remota, como sus proyectos con Bind4.0
- Energy Efficiency Optimization: IoT is transforming energy production, delivery, and consumption. Devices such as electric chargers, inverters, and switches connected through IoT gateways deliver advanced analytics and rich datasets. This allows energy companies to manage assets dynamically, reduce maintenance costs, and improve safety. Barbara IoT has developed industrial IoT solutions to monitor the performance of solar panels with high granularity.
- Inteligencia en el edge: la computación en el edge procesa los datos en el origen antes de enviar solo los resultados esenciales a la nube, lo que ahorra ancho de banda y costes. Esto es común en cámaras inteligentes que detectan, identifican o cuentan objetos y personas. Desde la crisis del COVID-19, la inteligencia en el edge ha ganado demanda para la monitorización estratégica, como en accesos a escuelas o centros comerciales. Barbara OS apoya este enfoque con conectividad segura y aplicaciones de edge en contenedores desplegadas de forma remota.
- Predictive Failure Detection: IoT and AI are key enablers for predictive maintenance. Detecting failures early and resolving them before they happen can save up to 40% in maintenance costs. Predictive maintenance improves efficiency by identifying recurring errors, using historical data to forecast long term failures. This often involves vibration, motion, sound, or temperature sensors securely connected through platforms like Barbara OS.
- Monitoreo en el sector ferroviario: las redes ferroviarias actuales requieren miles de sensores para supervisar el estado de los materiales y el rendimiento de las vías. Estos datos son fundamentales para los equipos de operación y mantenimiento. Aunque se trata de un sector altamente regulado, el IoT está penetrando poco a poco en la industria ferroviaria. Barbara OS garantiza el cumplimiento de las normas de seguridad ferroviaria al tiempo que permite un despliegue de IIoT eficiente y seguro.